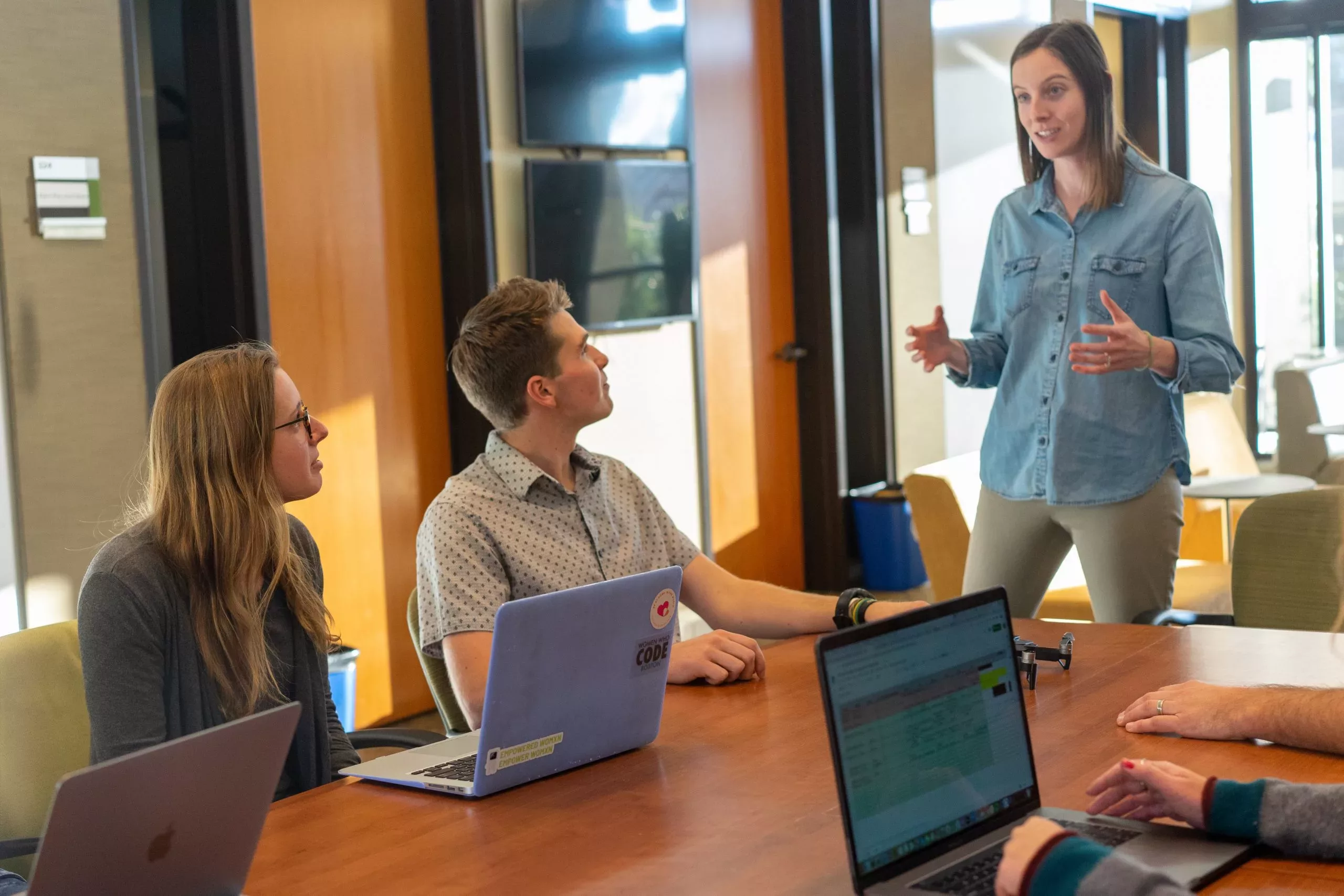
The shift towards remote work has become a prevailing trend in today’s fast-paced business landscape.
Organizations increasingly use remote collaboration tools to ensure seamless collaboration and productivity among dispersed teams.
These digital solutions allow teams to communicate, share files, and collaborate on projects regardless of geographical barriers.
This post will explore the seven best remote collaboration tools, delving into their definitions, historical context, key features, benefits, disadvantages, and real-world examples.
1. Slack:
Definition: Slack is a cloud-based team communication and collaboration platform that facilitates real-time messaging, file sharing, and integration with various third-party apps.
History: Stewart Butterfield, Eric Costello, Cal Henderson, and Serguei Mourachov launched Slack in 2013 as an internal tool for their gaming company. It soon evolved into a standalone product, revolutionizing team communication.
Features: Channels for organized discussions, direct messaging, file sharing, app integrations, and voice/video calls.
Benefits: Improved team communication, enhanced productivity, quick information exchange, and streamlined workflow.
Disadvantages: Potential information overload and dependence on notifications leading to distractions.
2. Microsoft Teams:
Definition: Microsoft Teams is a collaboration platform integrated into Microsoft 365 that offers chat, video conferencing, file sharing, and project management capabilities.
History: Microsoft Teams was introduced in 2017 as a response to the growing demand for a comprehensive team collaboration tool.
Features: Chat-based workspace, video conferencing, file collaboration, app integrations, and collaborative project management.
Benefits: Seamless integration with Microsoft 365 apps, robust security features, and a unified communication platform.
Disadvantages: Limited integration options with non-Microsoft apps.
3. Zoom:
Definition: Zoom is a video conferencing platform that enables remote teams to conduct virtual meetings, webinars, and conference calls.
History: Founded in 2011 by Eric Yuan, Zoom quickly gained popularity as a reliable video conferencing solution.
Features: High-quality video and audio conferencing, screen sharing, virtual backgrounds, breakout rooms, and recording.
Benefits: Efficient virtual meetings, ease of use, scalability for large conferences, cross-platform support.
Disadvantages: Privacy and security concerns (past incidents of “Zoom bombing”).
4. Google Workspace (formerly G Suite):
Definition: Google Workspace is a suite of cloud-based productivity tools, including Gmail, Google Drive, Google Docs, and Google Meet, facilitating remote collaboration and communication.
History: Launched as Google Apps in 2006, it was later rebranded as G Suite and, in 2020, renamed Google Workspace.
Features: Email, cloud storage, collaborative document editing, video conferencing, and shared calendars.
Benefits: Real-time collaboration on documents, seamless integration with Google services, and easy file sharing.
Disadvantages: Limited offline access and potential data privacy concerns.
5. Trello:
Definition: Trello is a visual project management tool that uses boards, lists, and cards to organize tasks and facilitate team collaboration.
History: Trello was released in 2011 by Fog Creek Software and later acquired by Atlassian.
Features: Kanban-style task management, customizable boards, task assignments, due dates, and integrations with other apps.
Benefits: Easy project tracking, visual organization, flexibility for different workflows.
Disadvantages: Might be less suitable for complex project management.
6. Asana:
Definition: Asana is a versatile work management platform that helps teams track tasks, projects, and workflows efficiently.
History: Asana was founded in 2008 by former Facebook executives Dustin Moskovitz and Justin Rosenstein.
Features: Task management, project tracking, deadlines, collaboration features, and integrations.
Benefits: Effective project planning, streamlined task assignment, centralized communication.
Disadvantages: It is complex for first-time users and has limited free version features.
7. Dropbox:
Definition: Dropbox is a popular cloud-based file storage and sharing service that enables teams to access and collaborate on files from anywhere.
History: Dropbox was founded in 2007 by Drew Houston and Arash Ferdowsi.
Features: File synchronization, file sharing, team folders, document collaboration, and integrations.
Benefits: Easy file access, automatic device syncing, seamless collaboration on shared files.
Disadvantages: Limited storage space for free accounts, version control can be improved.
Conclusion:
As remote work continues to thrive, the importance of remote collaboration tools cannot be overstated.
The seven tools mentioned above—Slack, Microsoft Teams, Zoom, Google Workspace, Trello, Asana, and Dropbox—have revolutionized teamwork, ensuring enhanced productivity and efficient communication.
Each tool has unique features and advantages, making it crucial for organizations to select the one that best suits their needs and workflows.
With these powerful remote collaboration tools, teams can conquer geographical barriers and work together seamlessly to achieve shared goals.