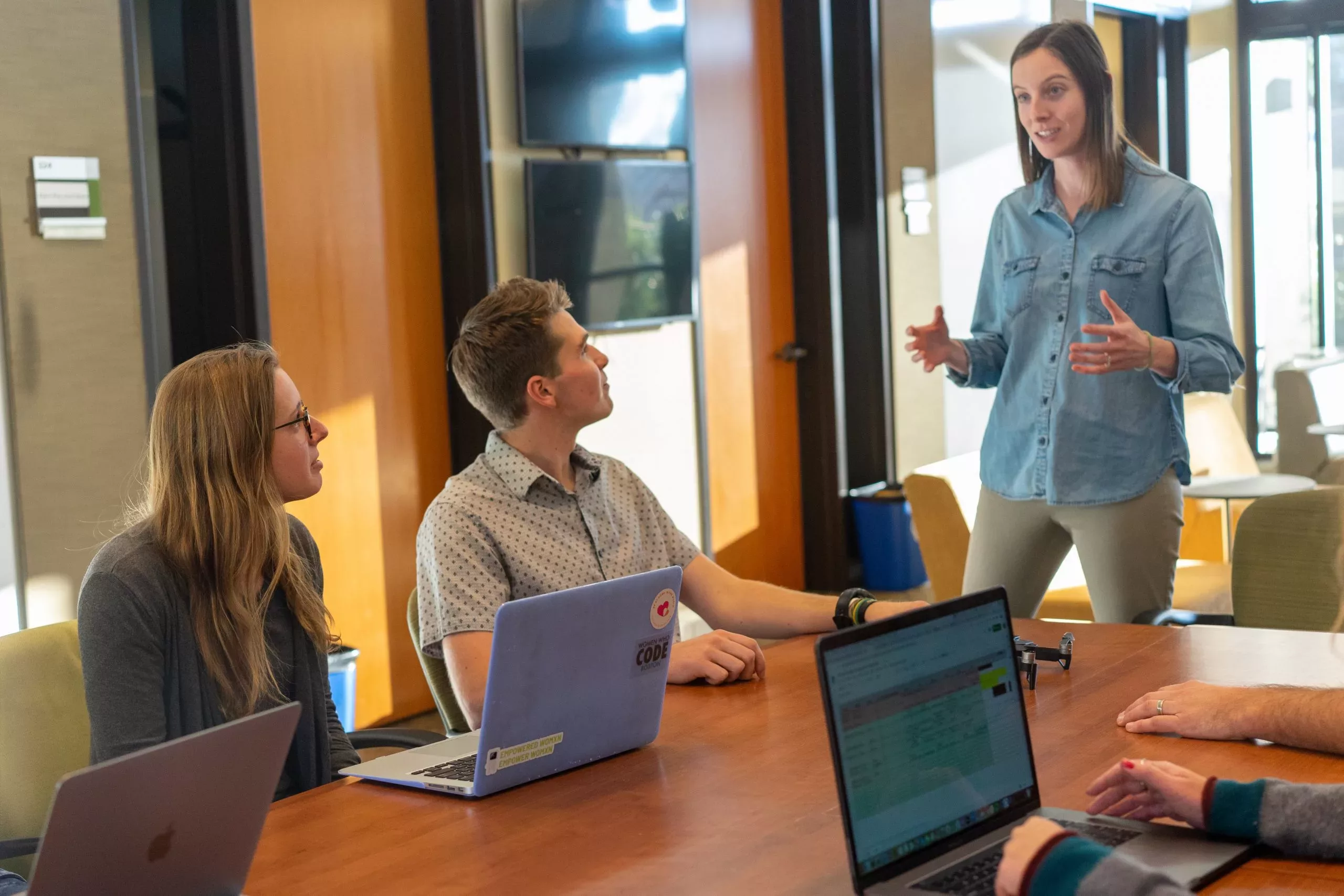
The key to competitive success lies in offering quality products and delivering exceptional customer experiences.
Retail training empowers employees with the knowledge, skills, and expertise to thrive and meet consumers’ ever-changing demands.
This comprehensive guide delves into retail training, offering valuable insights into its definition, benefits, features, and potential disadvantages.
Retail training is the cornerstone of a successful retail business. It enhances customer service, boosts sales performance, and fosters a motivated and skilled workforce.
Let’s embark on a journey through the intricacies of retail training and discover how it can revolutionize how your business operates and thrives in this dynamic industry.
Guide to Retail Training:
1. Definition of Retail Training:
Retail training refers to imparting knowledge, skills, and competencies to individuals in the retail industry.
It aims to equip employees with the necessary tools and techniques to excel in their roles, meet customer needs, and contribute to the overall success of the retail business.
Retail training covers various aspects, including product knowledge, customer service, sales techniques, merchandising, and operational procedures.
2. Benefits of Retail Training:
a. Improved Customer Service: Well-trained retail staff can provide better customer service, increasing customer satisfaction and loyalty.
b. Increased Sales Performance: Retail training enhances sales techniques, enabling employees to upsell and cross-sell effectively.
c. Enhanced Product Knowledge: Informed employees can educate customers about products, boosting their confidence in purchasing.
d. Reduced Employee Turnover: Training shows employees that their employer invests in their development, leading to higher job satisfaction and lower turnover rates.
e. Efficient Operations: Retail training streamlines operational procedures, resulting in more efficient and effective day-to-day processes.
f. Improved Employee Morale: Proper training increases employee confidence and motivation, improving overall morale.
g. Compliance and Safety: Training ensures employees adhere to safety regulations and comply with company policies.
3. Features of Retail Training:
a. Role-Specific Training: Tailored training programs based on the specific roles and responsibilities within the retail business, such as sales associate, cashier, merchandiser, etc.
b. Interactive Learning: Engaging training methods, including simulations, role-playing, and real-life scenarios, to foster active learning and skill application.
c. Continuous Development: Ongoing training to keep employees updated with the latest industry trends, products, and techniques.
d. Performance Evaluation: Regular assessments are used to gauge training effectiveness and identify areas for improvement.
e. E-Learning and Mobile Training: Utilizing digital platforms and mobile devices for convenient and accessible learning.
f. Soft Skills Training: Besides technical skills, training on soft skills like communication, problem-solving, and empathy is crucial for excellent customer service.
4. Disadvantages of Retail Training:
a. Cost: Implementing comprehensive retail training programs can be expensive, especially for small businesses with limited budgets.
b. Time-Consuming: Training may require employees to spend time away from their regular duties, impacting daily operations.
c. Employee Resistance: Some employees may resist training or be reluctant to adapt to new methods, hindering the program’s effectiveness.
d. Training Turnover: If employees leave shortly after training, the company may not fully benefit from their newly acquired skills.
5. Examples of Retail Training:
a. Customer Service Training: This training teaches employees how to engage with customers, handle complaints, and create positive shopping experiences.
b. Sales Techniques Training: Equips employees with effective selling strategies and the art of persuasion.
c. Product Knowledge Training: Provides comprehensive information about the products sold, their features, and benefits.
d. Visual Merchandising Training: Instruct employees on arranging displays to maximize product visibility and appeal.
e. Point of Sale (POS) Training: Familiarize employees with the POS system to ensure efficient transactions.
f. Loss Prevention Training: Educates employees on preventing theft and ensuring store security.
g. Health and Safety Training: Ensures employees follow safety protocols, reducing accidents and liabilities.
Remember, practical retail training is an ongoing process that adapts to industry changes, customer expectations, and the evolving needs of the workforce.
Investing in the development of retail employees can significantly impact the success and growth of a retail business.