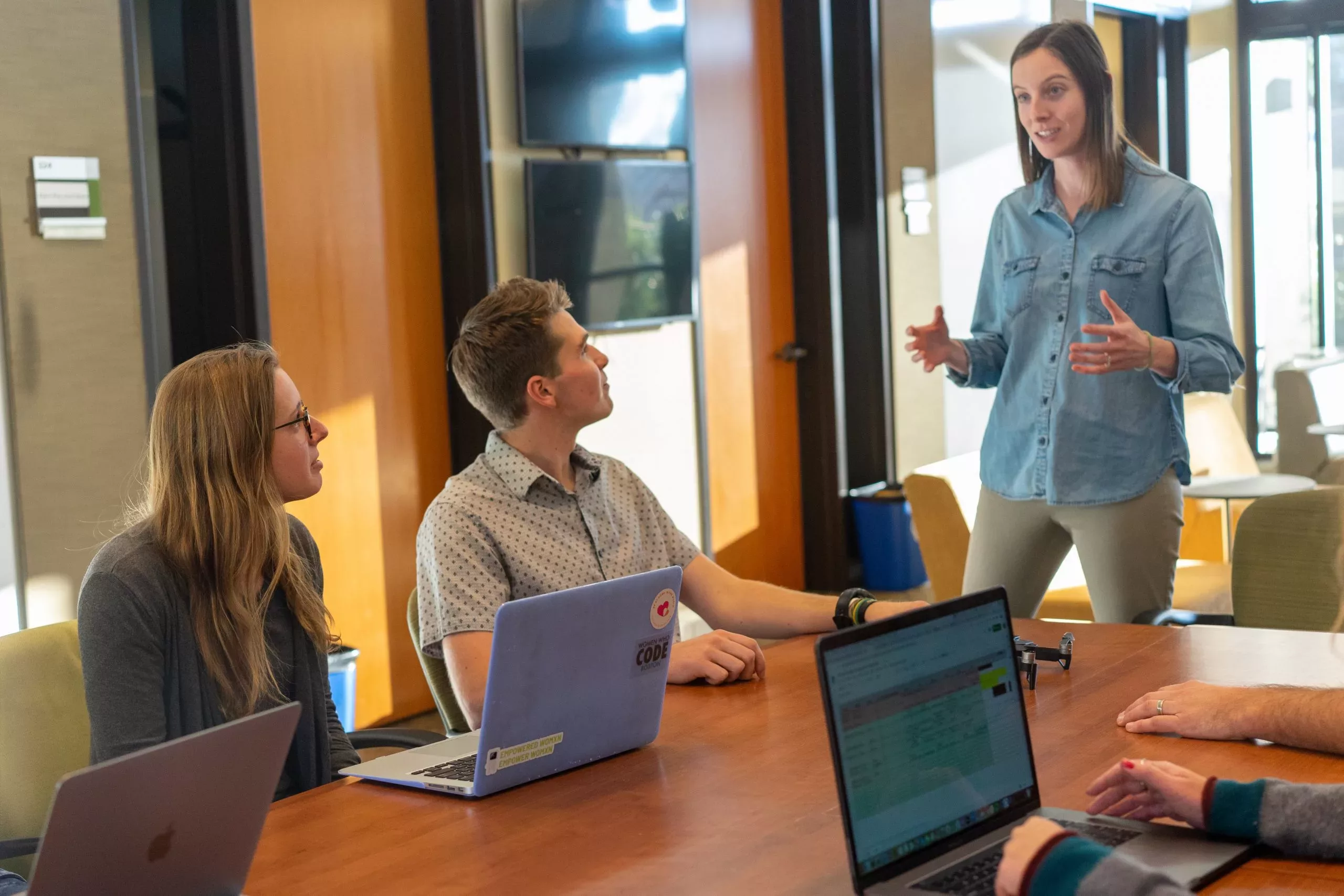
More flexible and efficient approaches are gradually replacing the traditional 9-to-5 work model.
Asynchronous work is one such approach that has gained significant attention within employee training courses in recent years.
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of asynchronous work, its benefits, best practices, and everyday usage in the workplace.
Supercharge Your Training Courses – A Special Offer From Oak Innovation
Definition and Background
Asynchronous work refers to a work style where employees are not required to be present or available simultaneously.
Instead, they can choose when and where they work as long as they meet their deadlines and deliverables.
This approach gives individuals more control over their schedules and promotes a focus on outcomes rather than hours worked.
The concept of asynchronous work has gained prominence due to technological advancements, which enable seamless communication and collaboration across different time zones and locations.
It has become increasingly important in a globalized world where teams are often distributed across various regions.
Differences between Asynchronous and Synchronous Work
- Time Flexibility: Asynchronous work allows employees to choose their working hours, while synchronous work requires everyone to be available simultaneously.
- Location Independence: Asynchronous work enables individuals to work from anywhere, while synchronous work often requires physical presence in a specific location.
- Reduced Interruptions: Asynchronous work minimizes interruptions from real-time communication, allowing for focused and uninterrupted work. Synchronous work involves immediate responses and can be more prone to distractions.
- Global Collaboration: Asynchronous work facilitates collaboration across different time zones, making it easier for teams to work together regardless of geographical boundaries. Synchronous work may pose challenges when coordinating across time differences.
- Increased Autonomy: Asynchronous work empowers employees to manage their time and prioritize tasks, fostering a sense of autonomy. Synchronous work often involves more direct supervision and immediate decision-making.
- Enhanced Work-Life Balance: Asynchronous work offers greater flexibility, enabling individuals to balance their personal and professional commitments better. Synchronous work may require strict adherence to fixed schedules, potentially impacting work-life balance.
Why Companies Are Interested in Asynchronous Work
Companies are increasingly interested in asynchronous work due to several reasons:
- Global Talent Pool: Asynchronous work allows organizations to tap into a diverse talent pool across different time zones and locations, enabling access to specialized skills and expertise.
- Increased Productivity: Asynchronous work promotes focused and uninterrupted work, enhancing productivity and efficiency.
- Cost Savings: Asynchronous work reduces the need for physical office spaces and associated expenses, resulting in potential cost savings for companies.
- Employee Satisfaction: Asynchronous work provides employees greater flexibility and autonomy, increasing job satisfaction and retention.
- Improved Collaboration: Asynchronous work encourages effective communication and collaboration, as teams must document their work and share information transparently.
- Business Continuity: Asynchronous work ensures that work can progress even during unforeseen circumstances, such as natural disasters or disruptions in transportation.
Best Practices for Asynchronous Work
Clear Communication: Establish communication channels and guidelines for effective information sharing and collaboration.
- Importance: Clear communication helps avoid misunderstandings and ensures everyone is on the same page, even though they work at different times.
- Achievement: Utilize project management tools, asynchronous messaging platforms, and shared documentation to facilitate communication.
Set Expectations and Deadlines: Clearly define each task or project’s expectations, deliverables, and deadlines.
- Importance: Setting expectations and deadlines helps maintain accountability and ensures the timely completion of work.
- Achievement: Use project management software or task management tools to assign tasks, set deadlines, and track progress.
Document Work and Decisions: Encourage team members to document their work, decisions, and progress to facilitate collaboration and knowledge sharing.
- Importance: Documenting work ensures transparency, enables easy access to information, and helps new team members quickly get up to speed.
- Achievement: Utilize shared document repositories, wikis, or knowledge management systems to store and organize information.
Respect Time Zones and Availability: When scheduling meetings or requesting immediate responses, be mindful of different time zones and individual availability.
- Importance: Respecting time zones and availability promotes work-life balance and avoids unnecessary disruptions.
- Achievement: Use scheduling tools that consider time zone differences and allow team members to indicate their availability.
Encourage Self-Management and Autonomy: Foster a culture of trust and empower employees to manage their time and prioritize tasks.
- Importance: Encouraging self-management and autonomy boosts motivation, engagement, and accountability.
- Achievement: Provide clear goals, regular feedback, and opportunities for skill development to support employees in managing their work effectively.
Promote Collaboration and Feedback: Encourage regular feedback, virtual brainstorming sessions, and asynchronous discussions to foster a collaborative environment.
- Importance: Collaboration and feedback enhance creativity, innovation, and team cohesion.
- Achievement: Utilize collaboration tools, discussion forums, and feedback platforms to facilitate virtual collaboration.
Establish Clear Channels for Urgent Communication: Define urgent or time-sensitive communication protocols to ensure quick response times when necessary.
- Importance: Urgent communication channels help address critical issues promptly, even in an asynchronous work environment.
- Achievement: Implement instant messaging platforms or designate specific communication channels for urgent matters.
Training and Support: Offer training to help employees adapt to asynchronous work practices and effectively utilize relevant tools.
- Importance: Training and support ensure that employees have the necessary skills and knowledge to thrive in an asynchronous work environment.
- Achievement: Conduct training sessions, provide resources, and offer ongoing support through dedicated channels or help desks.
Promote Work-Life Balance: Encourage employees to maintain a healthy work-life balance by setting boundaries and avoiding overworking.
- Importance: Promoting work-life balance improves employee well-being, reduces burnout, and enhances productivity.
- Achievement: Encourage employees to take breaks, establish clear boundaries between work and personal life, and provide resources for mental health support.
Regularly Evaluate and Adapt: Continuously assess the effectiveness of asynchronous work practices and make adjustments as needed.
- Importance: Regular evaluation and adaptation ensure that the chosen asynchronous work practices align with the organization’s evolving needs.
- Achievement: Collect employee feedback, monitor key performance indicators, and conduct periodic reviews to identify areas for improvement.
Common Usages of Asynchronous Work
Asynchronous work finds application in various scenarios, including:
- Remote Work: Asynchronous work enables individuals to work remotely, allowing companies to tap into a global talent pool and reduce geographical constraints.
- Flexible Schedules: Asynchronous work accommodates employees with different schedules and preferences, promoting work-life balance and accommodating personal commitments.
- Collaboration Across Time Zones: Asynchronous work facilitates collaboration among teams in different time zones, ensuring continuous progress and reducing delays.
- Project Management: Asynchronous work supports effective project management by allowing team members to work on tasks independently and asynchronously while still contributing to the overall project goals.
- Client Communication: Asynchronous work provides flexibility in client communication, allowing for thoughtful responses and reducing the need for immediate availability.
Examples of Asynchronous Work in the Workplace
- Email Communication: Sending and responding to emails allows for asynchronous communication, enabling individuals to address queries and share information conveniently.
- Shared Document Collaboration: Collaborating on shared documents, such as Google Docs or Microsoft Office 365, allows team members to work on the same project asynchronously and provides real-time updates and feedback.
- Task Management Tools: Task management tools like Trello or Asana enable teams to assign tasks, set deadlines, and track progress asynchronously, ensuring transparency and accountability.
- Discussion Forums: Creating discussion forums or using collaboration platforms like Slack or Microsoft Teams allows team members to engage in asynchronous discussions, share ideas, and seek feedback.
- Virtual Meetings and Webinars: Conduct virtual meetings or webinars asynchronously, where participants can access recorded sessions at their convenience, accommodating different schedules and time zones.
Features and Benefits of Asynchronous Work in Corporate Settings
Asynchronous work offers several features and benefits, including:
- Flexibility: Asynchronous work allows employees to choose their schedules and work from anywhere, promoting work-life balance and accommodating personal commitments.
- Increased Productivity: Asynchronous work promotes focused and uninterrupted work by minimizing interruptions and distractions, leading to enhanced productivity.
- Global Collaboration: Asynchronous work facilitates collaboration across different time zones, enabling teams to work together seamlessly regardless of geographical boundaries.
- Cost Savings: Asynchronous work reduces the need for physical office spaces, resulting in potential cost savings for companies.
- Employee Satisfaction: Asynchronous work gives employees greater autonomy and flexibility, increasing job satisfaction and retention.
- Business Continuity: Asynchronous work ensures that work can progress even during unforeseen circumstances, such as natural disasters or disruptions in transportation.
Summary
Asynchronous work is a flexible and efficient approach that empowers employees to work on their terms, regardless of time zones or locations.
By implementing best practices and leveraging appropriate tools, companies can harness the benefits of asynchronous work, such as increased productivity, global collaboration, and improved work-life balance.
Embracing asynchronous work can lead to a more agile and resilient workforce, enabling organizations to thrive in today’s dynamic business landscape.